In the realm of electrical and communication systems, the type of cable used can significantly impact performance, safety, and reliability. One such crucial type is concentric cable.
What is a Concentric Cable?
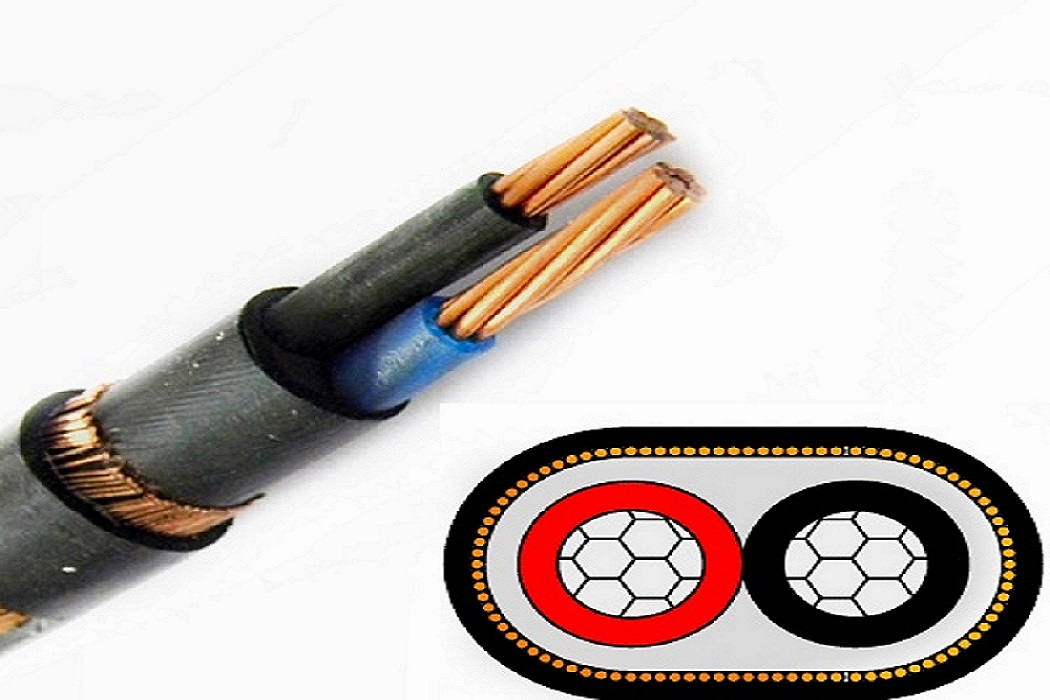
Concentric cable is a type of electrical cable characterized by its unique construction. It consists of one or more conductors, usually copper or aluminum, that are surrounded by layers of insulation and a concentric layer of conductors.
This design typically includes a central conductor, which is encased in an insulating layer. Surrounding this insulation is another layer of conductors, often in a helical or spiral configuration, followed by an outer insulating jacket.
Key Components of Concentric Cable
Central Conductor: The primary pathway for electrical current, usually made of copper or aluminum.
Insulating Layer: A non-conductive material that prevents short circuits and protects the conductors.
Concentric Conductors: Additional conductors that wrap around the insulation, providing added functionality and protection.
Outer Jacket: The final protective layer that shields the internal components from environmental factors.
Advantages of Concentric Cable
Improved Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Shielding: The concentric design helps in minimizing EMI, making it ideal for sensitive applications.
Enhanced Mechanical Protection: The layered structure provides robust protection against physical damage.
Better Grounding: The outer concentric conductors can serve as an effective grounding mechanism.
Types and Models of Concentric Cable
Concentric cables come in various types and models, each designed to meet specific requirements. The primary variations are based on the materials used, construction, and intended applications.
1. Copper Concentric Cable
Copper is renowned for its excellent electrical conductivity, making copper concentric cables a popular choice for many applications. These cables are often used in environments where superior conductivity and durability are essential.
Applications:
Power Distribution: Ideal for residential, commercial, and industrial power distribution.
Grounding Systems: Used in grounding applications due to copper’s excellent conductivity.
Control Systems: Suitable for control and instrumentation systems where precision is crucial.
2. Aluminum Concentric Cable
Aluminum concentric cables are lighter and often more cost-effective than their copper counterparts. While aluminum has lower conductivity than copper, it’s still sufficient for many applications, especially weight and cost are considerations.
Post time: Dec-06-2024